Replicate S3 buckets into another region
Setting up S3 bucket replication is a key method to achieve global buckets, allowing your data to be available across multiple regions.
When you replicate your S3 buckets, you continue to interact with your source bucket in its specific region.
What we'll be doing
By following this guide, you will achieve multi-region replication of your S3 bucket, enhancing data availability, durability, and disaster recovery capabilities.
- Review our existing module
- Create a Destination Bucket
- Create IAM Role and Policies for Replication
- Set Up Replication Configuration for S3 Bucket
Review our existing module
The first step is clone the Nitric repository and examine how the Nitric Terrraform provider provisions an S3 bucket.
git clone https://github.com/nitrictech/nitric
cd nitric
The AWS S3 module in the default Terraform provider performs the following tasks:
- Creates a unique ID for the S3 bucket to ensure unique naming.
- Provisions an S3 bucket with a unique name using the generated ID.
- Tags the bucket for identification.
- Grants S3 permission to invoke specified Lambda functions.
- Configures S3 bucket notifications to trigger Lambda functions based on specified events using dynamic blocks.
To begin our customization, we will start adding configuration to this module.
Create a Destination Bucket
Introduce a new variable into the aws/deploytf/.nitric/modules/bucket/variables.tf:
variable "replication_region" {
description = "The AWS region for the replication bucket"
type = string
default = "us-west-2"
}
Now we can edit our bucket/main.tf file and introduce a provider for the replication region:
provider "aws" {
alias = "replication"
region = var.replication_region
endpoints {
s3 = "https://s3.${var.replication_region}.amazonaws.com"
}
}
Then we can create our new destination bucket:
resource "random_id" "destination_bucket_id" {
byte_length = 8
}
resource "aws_s3_bucket" "destination" {
bucket = "tf-destination-bucket-${random_id.destination_bucket_id.hex}"
tags = {
"x-nitric-${var.stack_id}-name" = "tf-destination-bucket-${random_id.destination_bucket_id.hex}"
"x-nitric-${var.stack_id}-type" = "bucket"
}
provider = aws.replication
}
And enable versioning for both source and destination:
resource "aws_s3_bucket_versioning" "destination" {
bucket = aws_s3_bucket.destination.id
versioning_configuration {
status = "Enabled"
}
provider = aws.replication
}
resource "aws_s3_bucket_versioning" "source" {
bucket = aws_s3_bucket.bucket.id
versioning_configuration {
status = "Enabled"
}
}
Create IAM Role and Policies for Replication
First, we need to set up an IAM policy document detailing permissions needed for S3 replication.
data "aws_iam_policy_document" "assume_role" {
statement {
effect = "Allow"
principals {
type = "Service"
identifiers = ["s3.amazonaws.com"]
}
actions = ["sts:AssumeRole"]
}
}
# Generate a random id for the IAM role
resource "random_id" "iam_role_id" {
byte_length = 8
}
resource "aws_iam_role" "replication" {
name = "tf-iam-role-replication-${random_id.iam_role_id.hex}"
assume_role_policy = data.aws_iam_policy_document.assume_role.json
}
data "aws_iam_policy_document" "replication" {
statement {
effect = "Allow"
actions = [
"s3:GetReplicationConfiguration",
"s3:ListBucket",
]
resources = [aws_s3_bucket.bucket.arn]
}
statement {
effect = "Allow"
actions = [
"s3:GetObjectVersionForReplication",
"s3:GetObjectVersionAcl",
"s3:GetObjectVersionTagging",
]
resources = ["${aws_s3_bucket.bucket.arn}/*"]
}
statement {
effect = "Allow"
actions = [
"s3:ReplicateObject",
"s3:ReplicateDelete",
"s3:ReplicateTags",
]
resources = ["${aws_s3_bucket.destination.arn}/*"]
}
}
resource "aws_iam_policy" "replication" {
name = "tf-iam-role-policy-replication-${random_id.iam_role_id.hex}"
policy = data.aws_iam_policy_document.replication.json
}
resource "aws_iam_role_policy_attachment" "replication" {
role = aws_iam_role.replication.name
policy_arn = aws_iam_policy.replication.arn
}
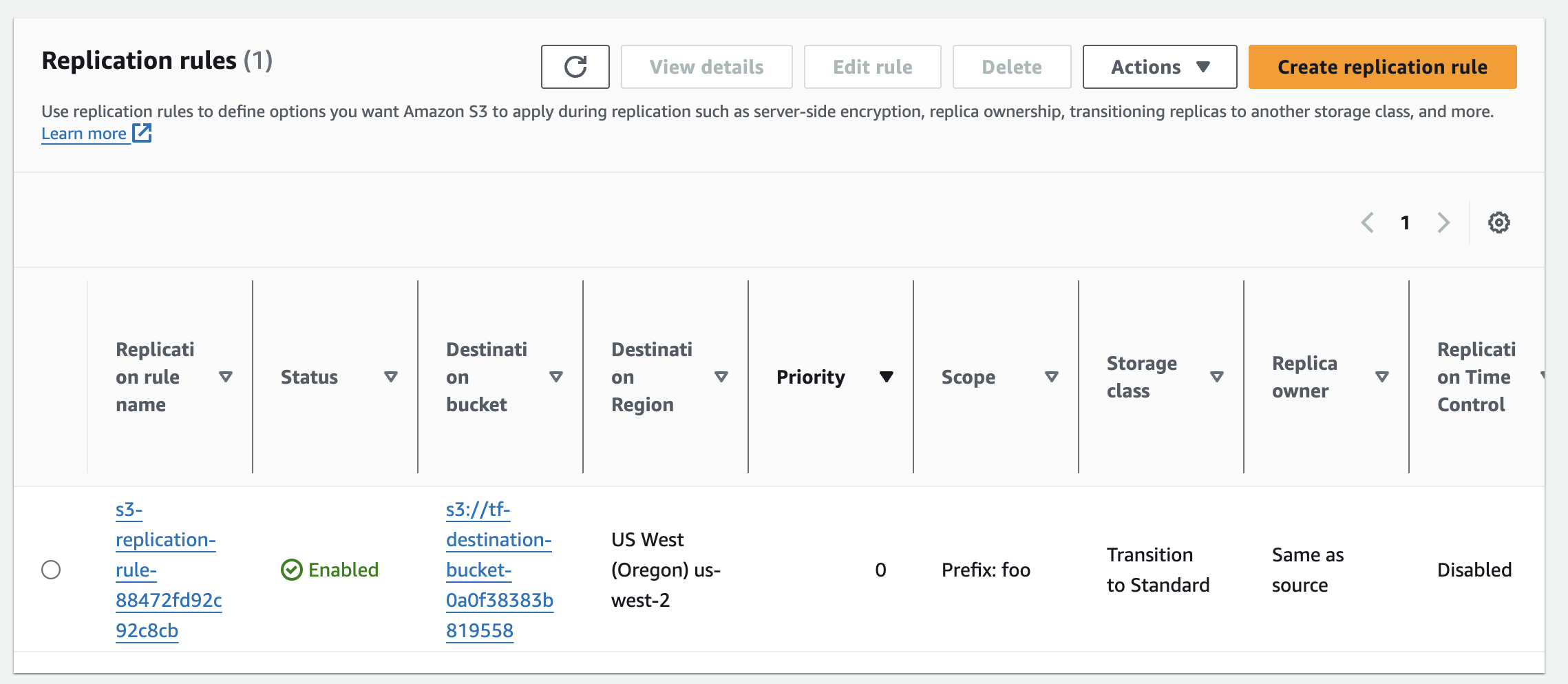
Set Up Replication Configuration for S3 Bucket
Next, we set up the replication configuration for our bucket.
resource "aws_s3_bucket_replication_configuration" "replication" {
depends_on = [
aws_s3_bucket_versioning.destination,
aws_s3_bucket_versioning.source
]
role = aws_iam_role.replication.arn
bucket = aws_s3_bucket.bucket.id
rule {
id = "s3-replication-rule-${random_id.bucket_id.hex}"
filter {
prefix = "foo"
}
status = "Enabled"
destination {
bucket = aws_s3_bucket.destination.arn
storage_class = "STANDARD"
}
delete_marker_replication {
status = "Enabled" # or "Disabled" based on your requirements
}
}
}
Building and using your updated provider
The Nitric project includes a make file that will build and install your provider as nitric/awstf@0.0.1 by default.
Run make install from the provider's root directory - nitric/cloud/aws
The provider can then be used directly in your project's stack file as follows.
# The nitric provider to use
provider: nitric/awstf@0.0.1
# The target aws region to deploy to
region: us-east-2
nitric stack new to create one.You'll also need to enable beta-providers in your Nitric project by adding the following to your project's nitric.yaml file:
preview:
- beta-providers
You can generate the Terraform code by running the following command:
nitric up
To deploy the application using Terraform, you can navigate into your Terraform stack directory and use the standard Terraform commands:
terraform init
terraform plan
terraform apply
You can examine your configuration by logging into the AWS console.